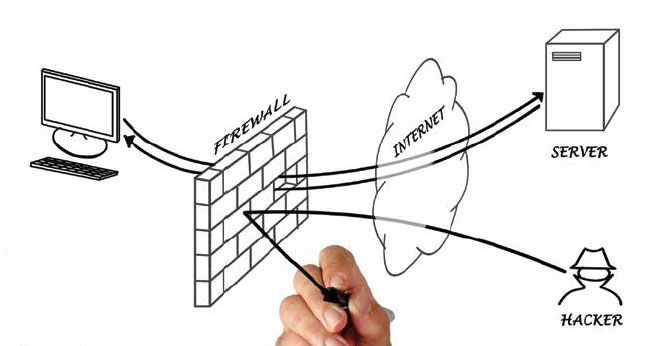
A firewall refers to a network device which blocks certain kinds of network traffic, forming a barrier between a trusted and an untrusted network. You can configure Windows firewall settings to send traffic only to the network you specify and block all others. For example, you can set up a firewall so that only the network you specify (or the network you have granted permission for) can send any specific types of network traffic.
Note Both the Windows Firewall and System Configuration screens control Network Connectivity, which you can use to define the rules for Windows and WAN connections, as well as Internet access. For more information about Configuring Internet Access, see Configuring the Internet Connection.
You can also control network traffic on a per-computer basis. When a user logs on to a computer, traffic that runs over the local network appears as an “Inbound” connection in the Network Connectivity Properties of the Computer dialog box. Traffic that runs over an untrusted network appears as an “Outbound” connection in the Network Connectivity Properties of the Computer dialog box.
If you add Windows firewall entries, Windows automatically applies the rules when the computer attempts to contact the internet. You can remove Windows firewall entries at any time.
To configure a Windows firewall to send certain types of network traffic only to the network you specify and to block all others, select the Firewall tab of the Properties dialog box. This dialog box includes several submenus for configuring your firewall.

